The Political Barometer is a software estimating political public opinion, by using polls and political tweets, which are collected and analysed daily. This analysis is based on Artificial Intelligence techniques (text sentiment analysis). Tweets collected refer to political parties that are currently forming Greek Parliament, in order to ensure data sufficiency (alphabetically ELLINIKI LISI, KKE, MERA25, ND, NIKI, PASOK-KINAL, PLEUSI ELEUFTHERIAS, SYRIZA). This software could substitute polls, offering the benefits below:
The Political Barometer research and Development work has been carried out by Computational Politics Special Interest Group (SIG) of the Computer Vision Machine Learning (AIIA.CVML) R&D group of the Artificial Intelligence and Information Analysis (AIIA) Laboratory of the Department of Informatics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, in the framework of the European project AI4Media during 2022-2024.
Numerous articles about the Political Barometer and its results have been published in both public and private Greek media outlets.
- Daily political public opinion analysis with immediate response to political stimulus.
- Higher accuracy than any traditional poll (accuracy ranges from 1.2% to 1.53%).
- Slightly better accuracy than the KASSIOPE poll aggregation method (accuracy 1.24%).
- The only cost is the X API fee for collecting tweets.
The Political Barometer research and Development work has been carried out by Computational Politics Special Interest Group (SIG) of the Computer Vision Machine Learning (AIIA.CVML) R&D group of the Artificial Intelligence and Information Analysis (AIIA) Laboratory of the Department of Informatics, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, in the framework of the European project AI4Media during 2022-2024.
Numerous articles about the Political Barometer and its results have been published in both public and private Greek media outlets.
The voters who have not decided their votes yet are distributed proportionally to all parties.
en.png)
en.png)
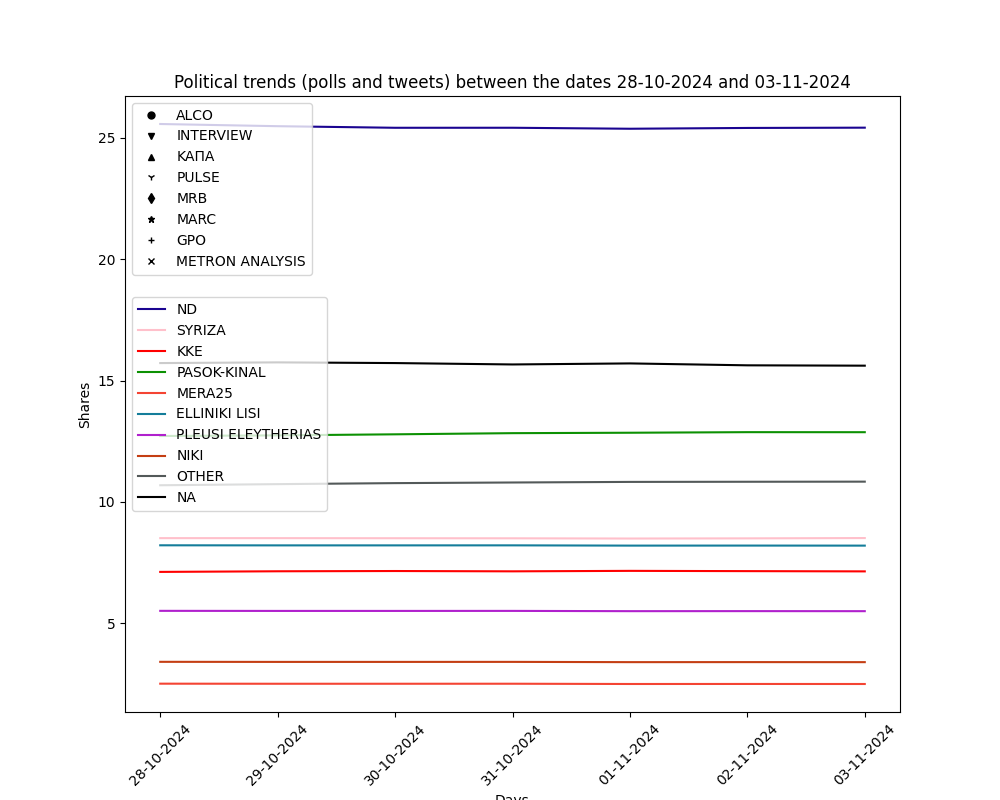
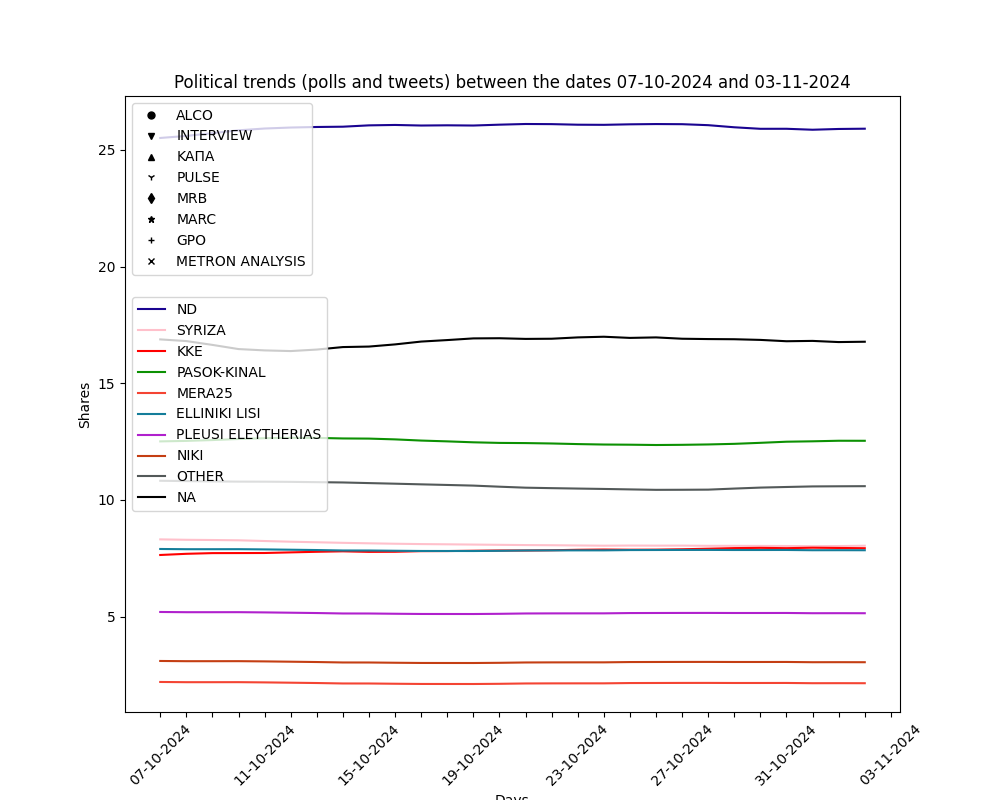
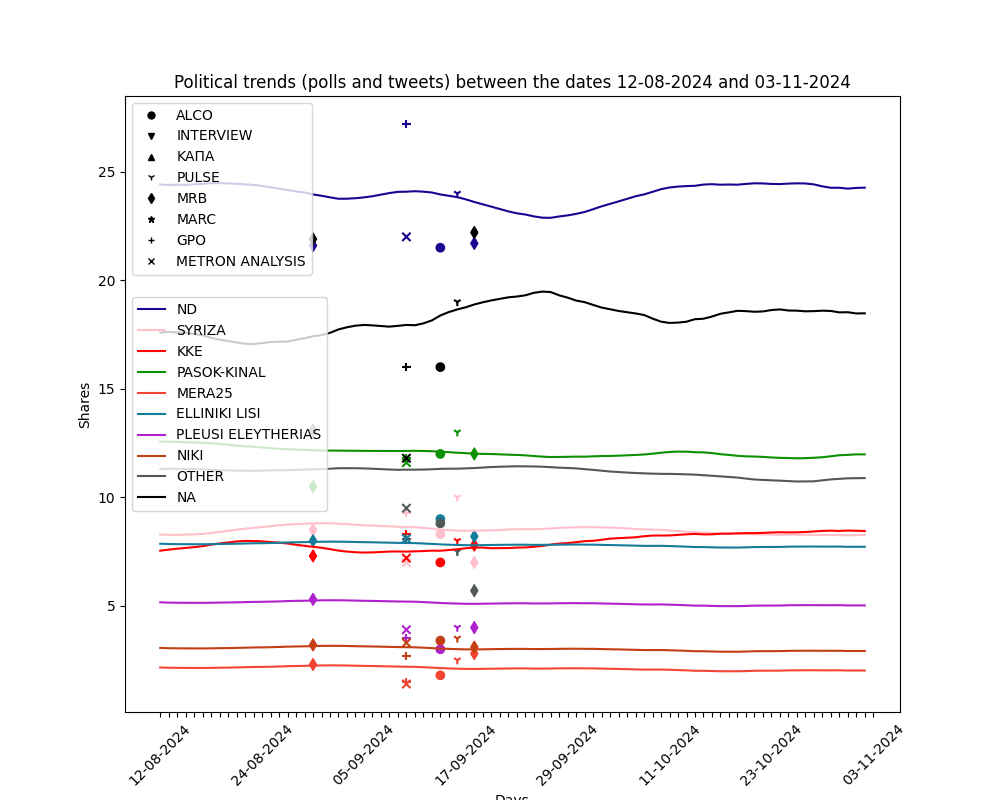
The current estimation on voting intention, based on the past weeks' political tweets.


The results of voting intention estimation per day for every political party is shown below. Our estimation uses a combination of PREVIOUS poll data and political tweet sentiment analysis. Polls are also provided with the symbols listed. Non-continuous line represents the period that the model DOES NOT takes new polls under consideration.
By using the arrows you can change viewing time period: a) past week, b) past month, c) past three months.
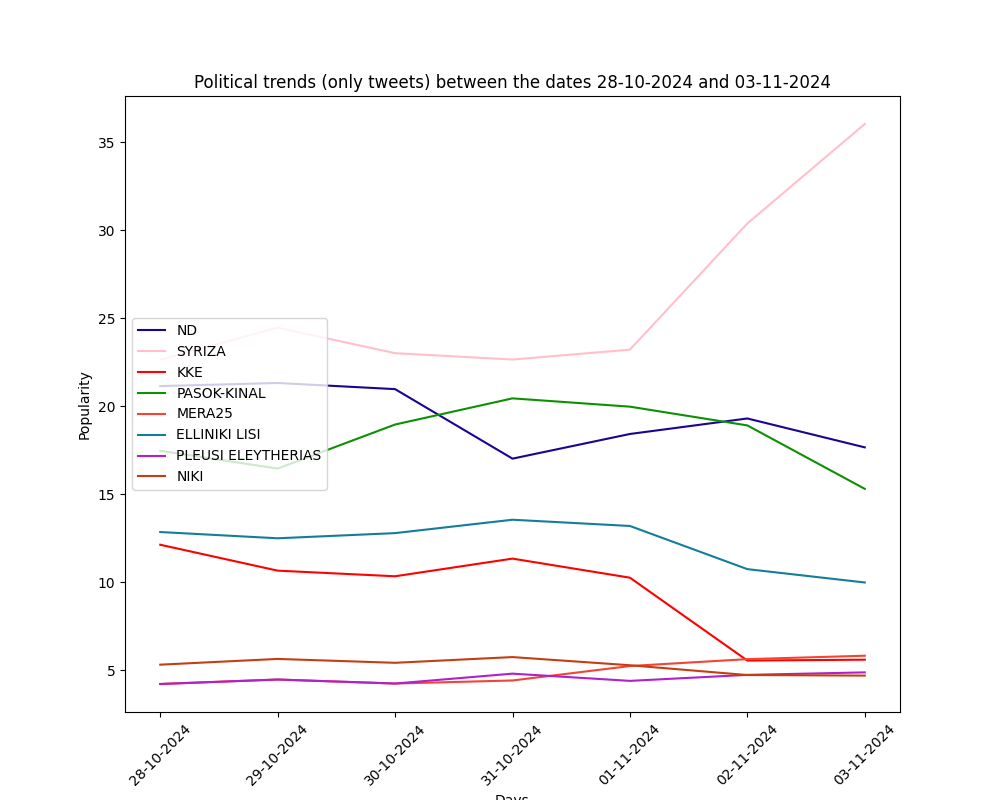
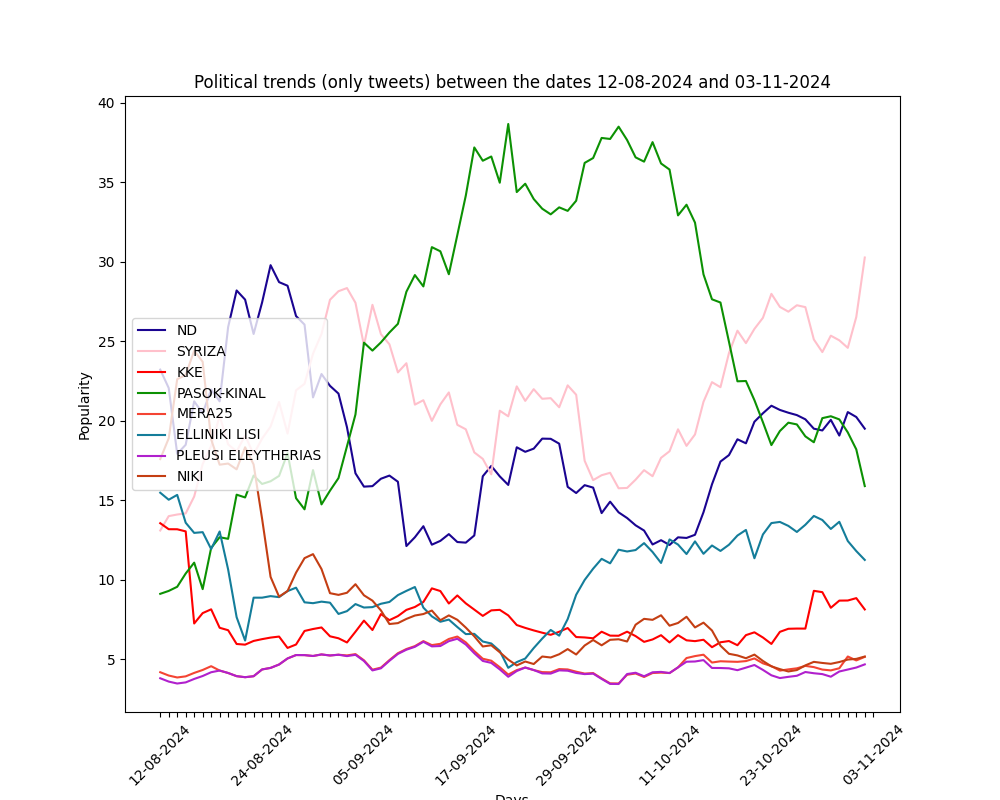
The graphs below show the estimation of voting intention merely from twitter data. Essentially, the negative tweets of every party are distributed to the rest of the parties according to their popularity (as defined by the share of their positive and neutral tweets).
This estimation presents significant sensitivity and ongoing political events have direct impact on it. It is emphasised here, that the individuals using twitter does not necessarily represent the general voting intention.
By using the arrows you can change viewing time period: a) past week, b) past month, c) past three months.
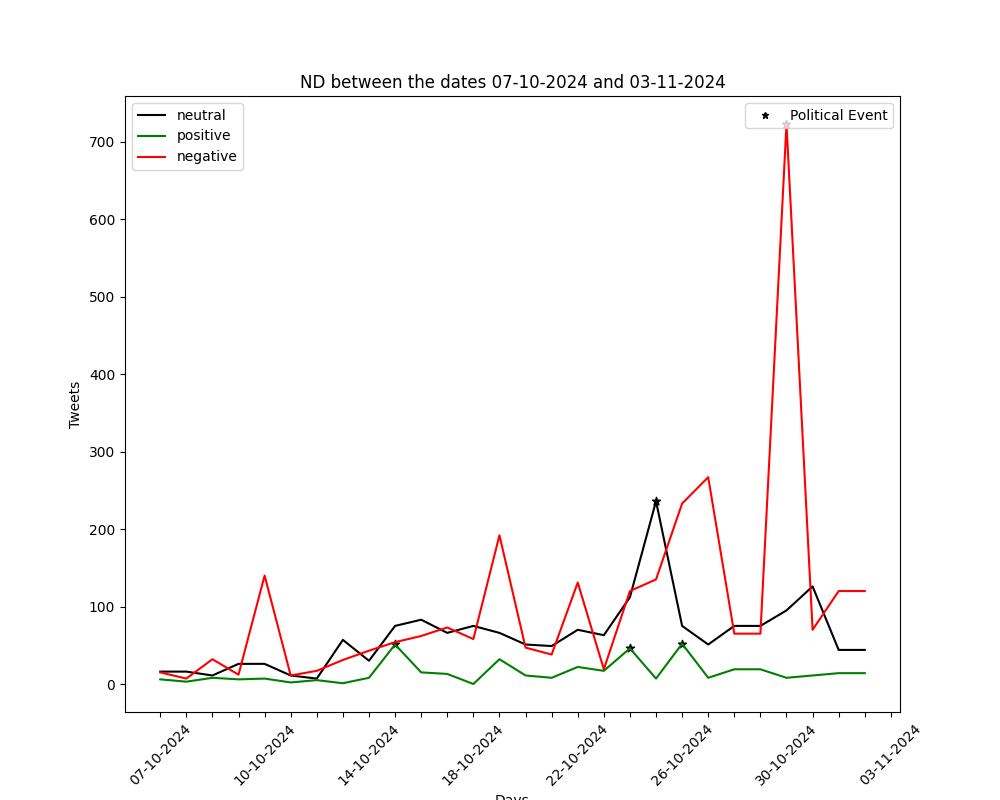
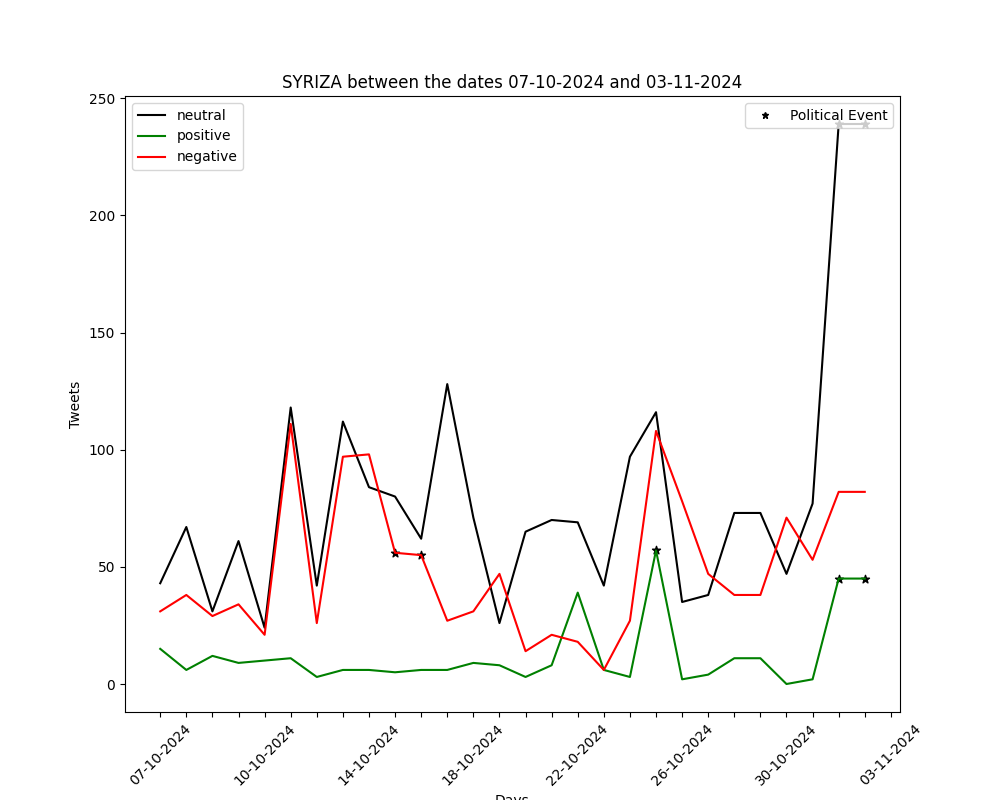
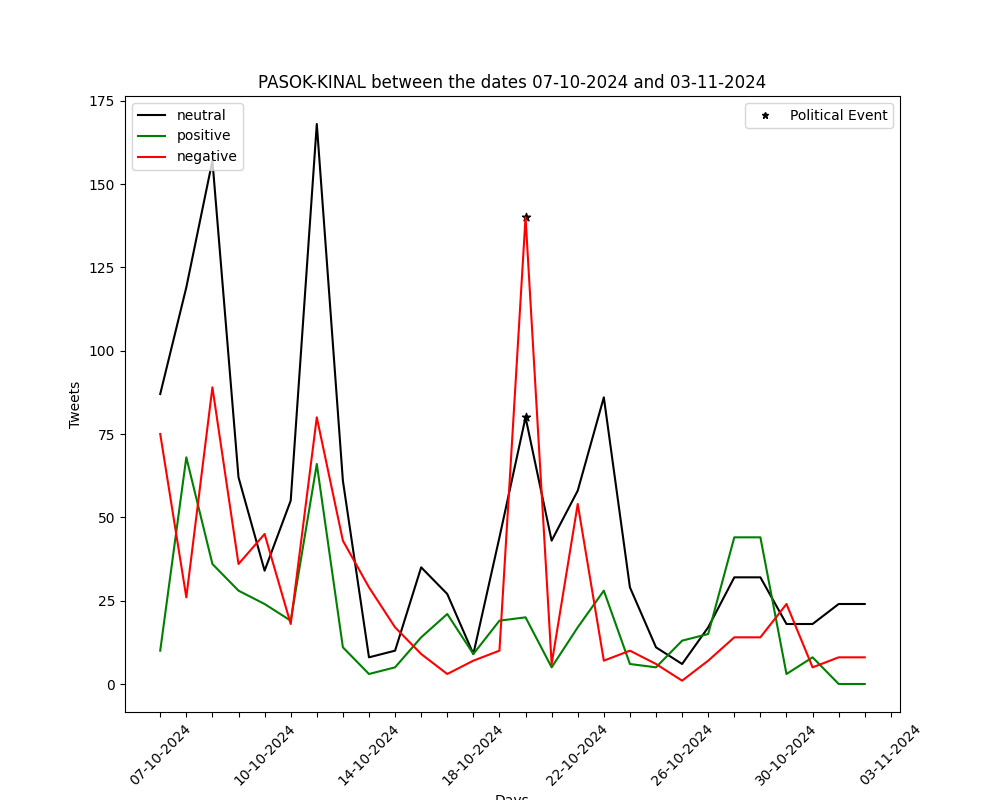
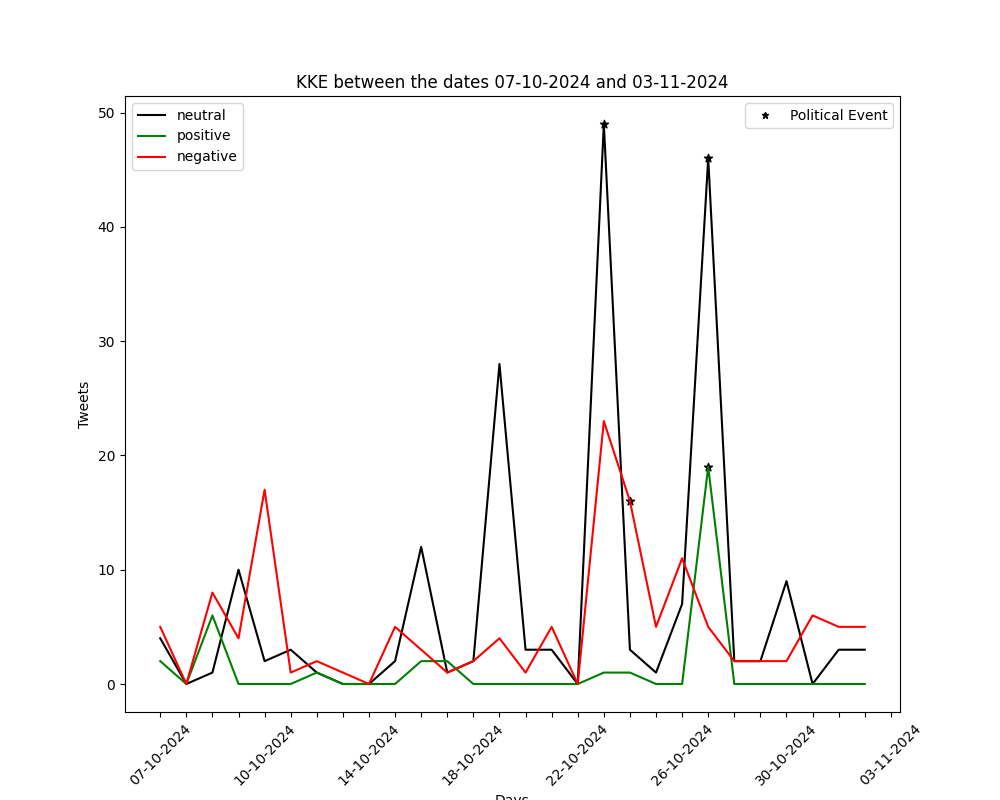
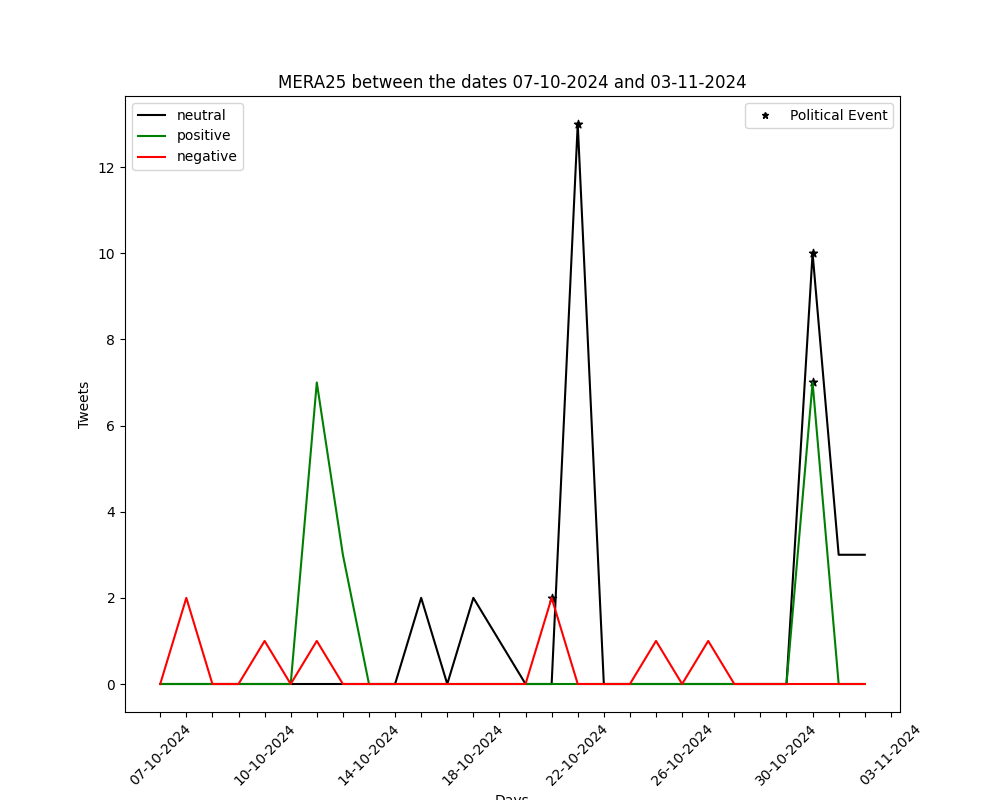
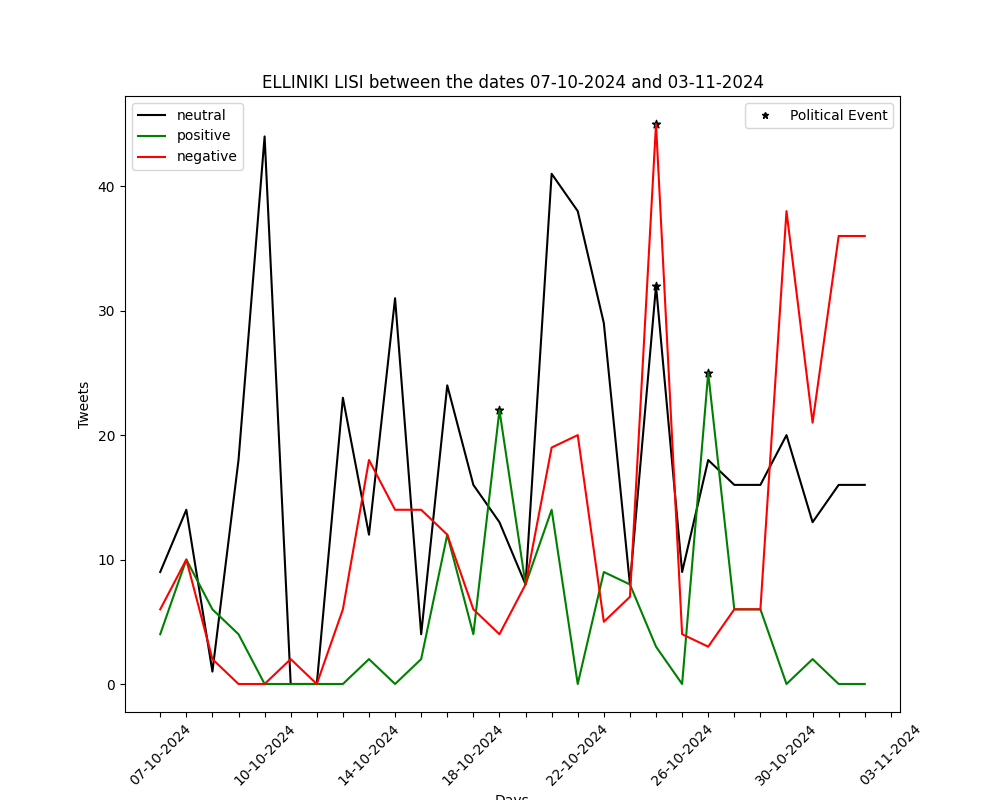
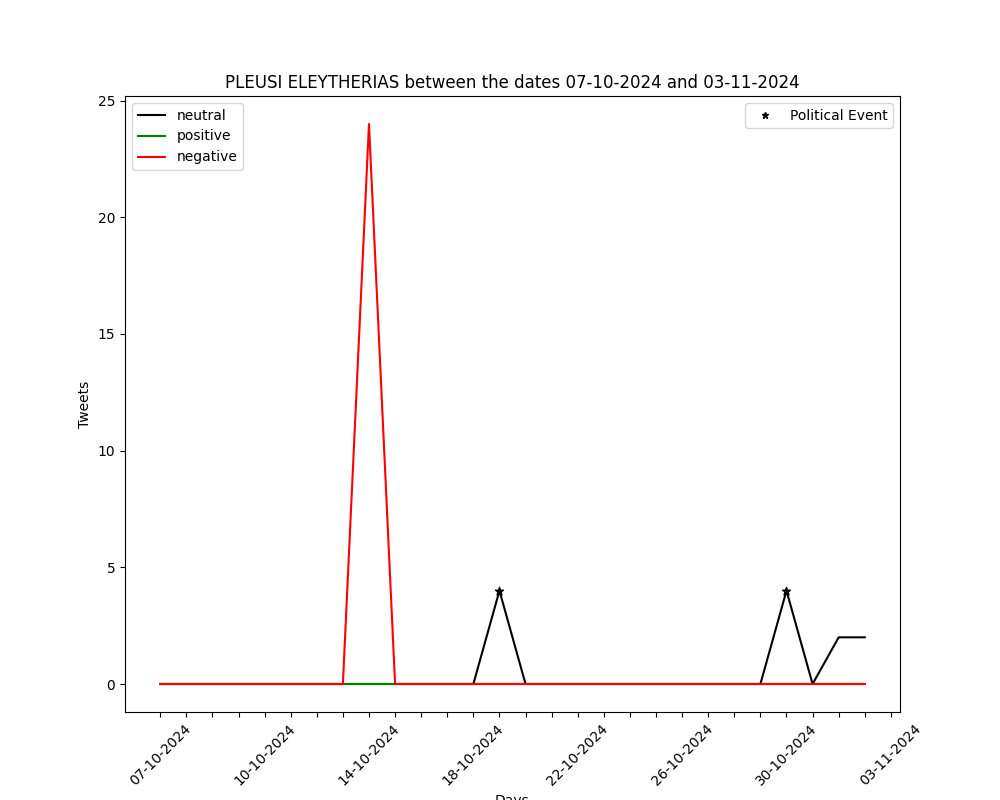
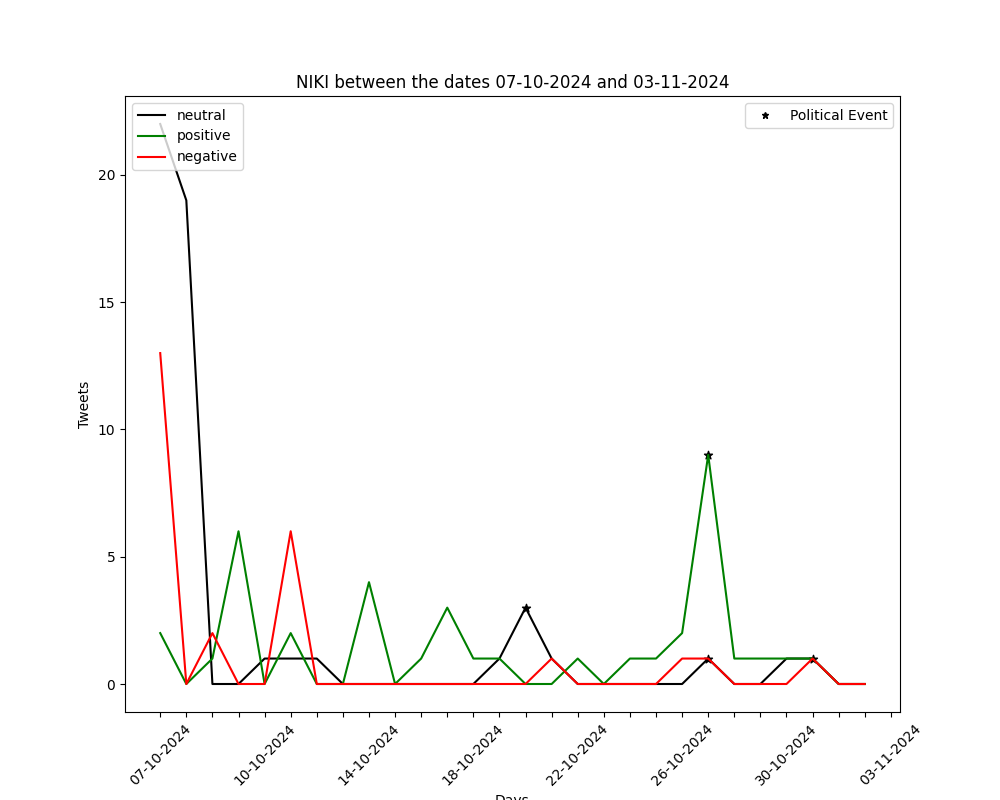
The graphs below show the number of positive-negative-neutral tweets per day for the past month (30 days). They are generated by automated political tweet analysis. The sentiment classification accuracy is approximately 82% after being compared to ground truth.
You can view the corresponding graph, for every party, by using the arrows.
26/2/2023: Greek MP Pavlos Polakis case (discussion for possible deletion)
1/3/2023: Vale of Tempe railway tragedy
28/3/2023: Announcement of the general election date (21/5/2023)
10/5/2023: Political leaders' debate.
21/5/2023: Parliamentary Elections
25/6/2023: Snap Parliamentary Elections
29/6/2023: Resignation of Alexis Tsipras from the leadership of SYRIZA
5/9/2023: Devastating floods in Thessaly caused by Storm Daniel
17/9/2023: SYRIZA Internal Elections (1st round)
24/9/2023: SYRIZA Internal Elections (2nd round)
8/10/2023: Regional and Municipal Elections
15/10/2023: 2nd round of Regional and Municipal Elections
9/6/2024: European Parliament Election
30/6/2024: Announcement of PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections
7/9/2024: Motion of no confidence against Stefanos Kasselakis
6/10/2024: PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections (1st round)
13/10/2024: PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections (2nd round)
1/3/2023: Vale of Tempe railway tragedy
28/3/2023: Announcement of the general election date (21/5/2023)
10/5/2023: Political leaders' debate.
21/5/2023: Parliamentary Elections
25/6/2023: Snap Parliamentary Elections
29/6/2023: Resignation of Alexis Tsipras from the leadership of SYRIZA
5/9/2023: Devastating floods in Thessaly caused by Storm Daniel
17/9/2023: SYRIZA Internal Elections (1st round)
24/9/2023: SYRIZA Internal Elections (2nd round)
8/10/2023: Regional and Municipal Elections
15/10/2023: 2nd round of Regional and Municipal Elections
9/6/2024: European Parliament Election
30/6/2024: Announcement of PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections
7/9/2024: Motion of no confidence against Stefanos Kasselakis
6/10/2024: PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections (1st round)
13/10/2024: PASOK – KINAL Internal Elections (2nd round)
Mean deviation for all political Greek parties in the European Parliament elections: 1.05%
Mean deviation for all political parties at the 25/6/2023 general elections: 1.1%
Mean Political Barometer deviation for all parties compared to opinion polls during 5/2022-5/2023: 0.95%
Mean deviation is small for smaller political parties and bigger for bigger ones, but very low on general.
By using more data the mean deviation was reduced significantly.
Mean deviation for all political parties at the 25/6/2023 general elections: 1.1%
Mean Political Barometer deviation for all parties compared to opinion polls during 5/2022-5/2023: 0.95%
Mean deviation is small for smaller political parties and bigger for bigger ones, but very low on general.
By using more data the mean deviation was reduced significantly.
I. Pitas – pitas@csd.auth.gr