Topic: Assuming 26-connectivity for 3D object (foreground) points, a voxel in the object is called a surface or border voxel if at least one of its 6-neighbors belong to the background.
An algorithm for finding the surface voxels of an object in a 3D image is described in [1] and illustrated for 2D image in the following figure:
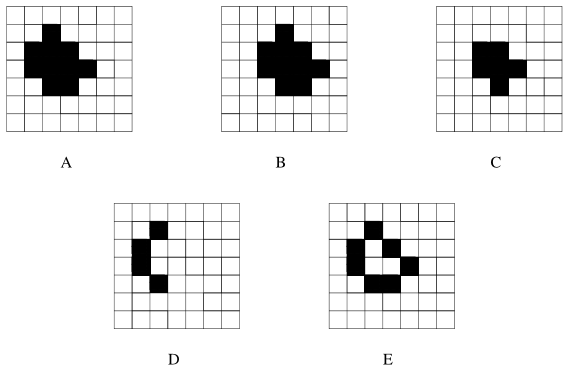
First, all pixels in image A are shifted right by one pixel to obtain image B. Then, the image C is obtained by evaluating the logical AND of images A and B. Finally, the image D is obtained by calculating the logical XOR of images C and A. This process is repeated for all four shifts directions (right, left, up, down) and the results are combined using the logical OR to obtain the final image E.
The algorithm for 3D case is exactly the same, with the only difference that the steps presented above need to be performed for six different shit directions (left, right, up, down, front, back).
Exercise: Implement the function for finding the surface of a 3D object. The function takes as input a 3D image (Numpy array) and returns a 3D image with the surface voxels.
Instructions and Material for solution: Click Code to download the exercise material.
References:
[1] Pitas I, Nikolaidis N, “3-D image processing algorithms”, Wiley (2000).
This exercise was developed by A. Kouzelis.
————————————————————————————————————–
For the solutions to the exercises, please contact koroniioanna@csd.auth.gr
