DESCRIPTION
Digital Signals and Systems are everywhere. Digital 1D signals, 2D signals (images) and 3D signals (video) encompass the vast majority of digital information nowadays in several disciplines:
- Digital Media, Social Media (music, images, video),
- Biomedical Signal/Image Analysis and Diagnosis,
- Autonomous cars, drones, marine vessels, robots
- Big Data Analytics,
- Internet and Communications (media broadcasting, streaming).
- Scientific signal acquisition of any sort, e.g., Remote Sensing, Environment Sensing, Geophysical Prospecting.
Digital Systems can model every aspect of the world, e.g., :
- Financial systems and Engineering
- Biomedical and Biology Systems
- Power plants
- Autonomous Systems and Robotics.
- Neural Networks.
- Social Networks, Complex Networks.
Much confusion exists nowadays in CVML literature, as even mature ML scientists have no background on Signals and Systems and confuse even basic notions, e.g., convolutions and correlations. SS principles are overviewed, while focusing on fast convolution algorithms, particularly on 2D convolution algorithms that are an absolute must for CNN libraries/frameworks and many computer vision tasks.
This CVML Web Module focuses on Signals and Systems and their applications. It starts with an Introduction to Signals and Systems. Then, a) Continuous-time Signals and Systems and b) Discrete-time Signals and Systems are presented. FIR and IIR systems are detailed. Signal Sampling is overviewed, as it provides the theoretical basis for A/D conversion and transformation of Continuous-time Signals to Discrete-time Signals. Various signals transform types are detailed, as they form the basis for signal processing and analysis: a) Laplace Transform; b) Fourier Transform; c) Orthogonal Signal Transforms; d) Fourier Series; e) Z Transform; f) Discrete Fourier Transform. Fast Fourier Transform. Fast 1D Convolution Algorithms provide the programming basis for fast linear system/filter implementations. State-Space Equations provide a very important prelude to RNN and LSTM neural networks.
LECTURE LIST
- Introduction to Signals and Systems
- Continuous-time Signals and Systems
- Discrete-time Signals and Systems
- Fourier Transform
- Orthogonal Signal Transforms. Fourier Series
- Laplace Transform
- Signal Sampling
- Z Transform
- Discrete Fourier Transform
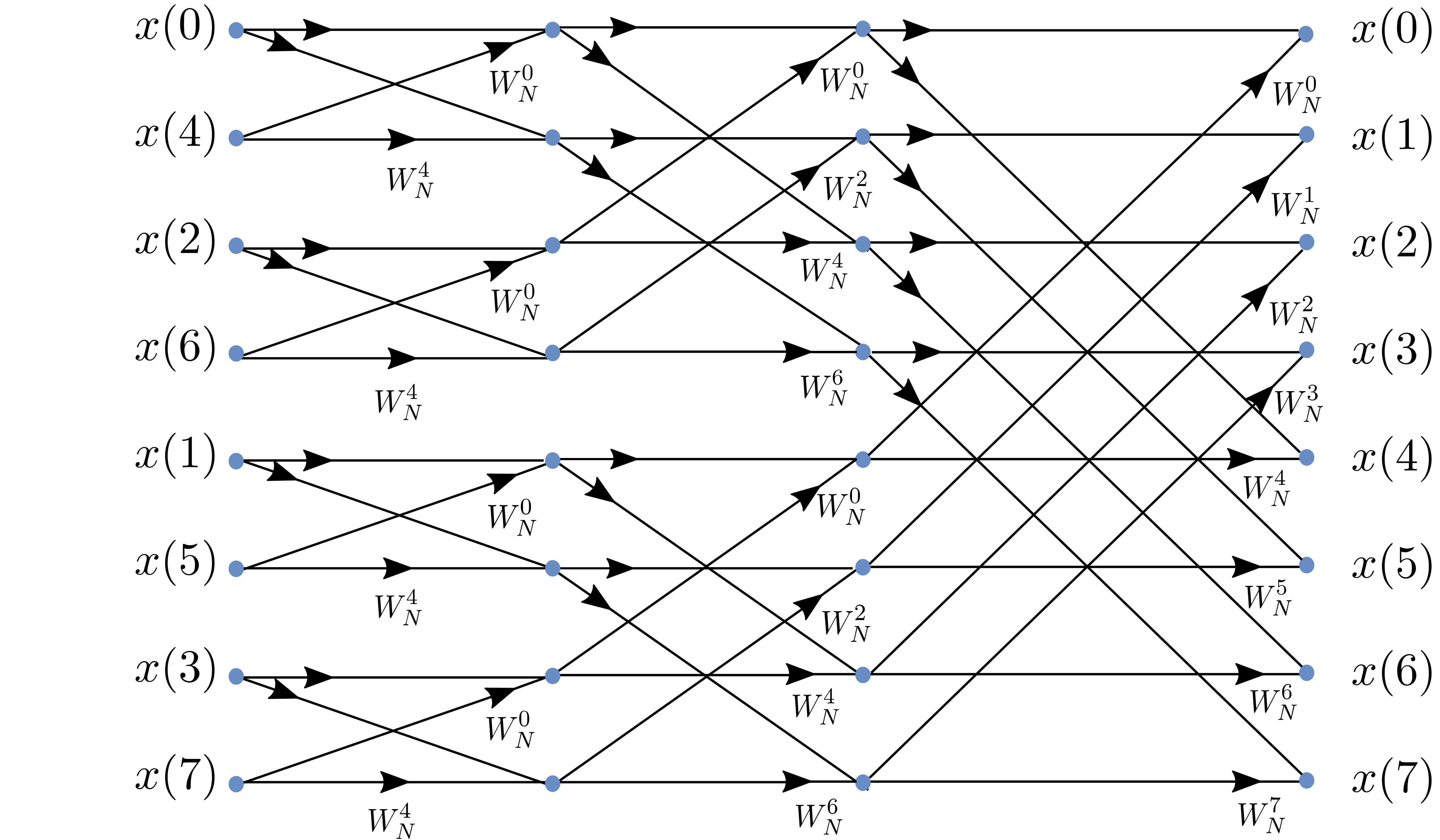
- Fast Fourier Transform
- State-Space Equations
CVML WEB LECTURE MODULE SCHEDULE
This module has been designed to be mastered within 1 month (or less), if you have proper background (at least early undergraduate student in an EE, ECE, CS, CSE or any Engineering or Exact Sciences Department).
We propose that you follow the above mentioned Lecture order. You may want to skip few Lectures that might not be of immediate interest to you for later study.
On average you can study 4 lectures per week. The related effort is as follows:
Lecture pdf study and filling the related understanding questionnaire: 1-2 hours per lecture (on average, depending on your background).
